how machine learning is changing art
From neural networks to deep learning, machine learning is changing just about every industry in the world – including art. The experimental projects below show how art and technology combine to blur the lines between disciplines and create something completely new.
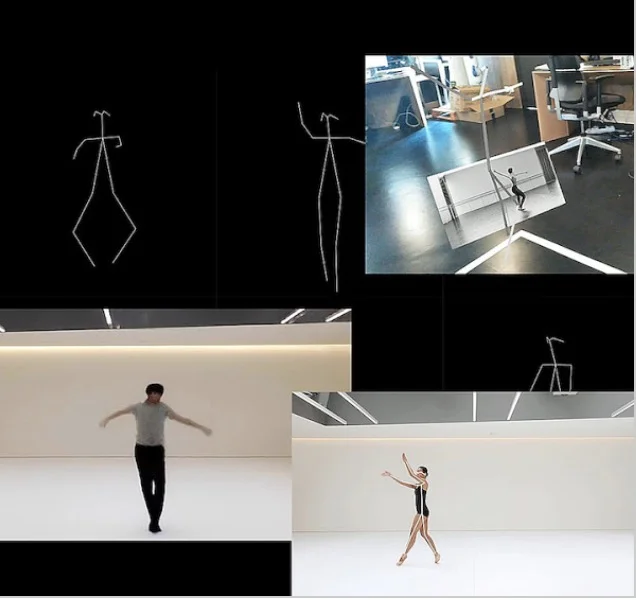
LIVING ARCHIVE
This machine learning project generates original movement inspired by Wayne McGregor’s 25-year archive of choreography. The result is a live dialogue between dancers and his body of work, immortalizing the style of his repertoire and generating novel experiences in the process.
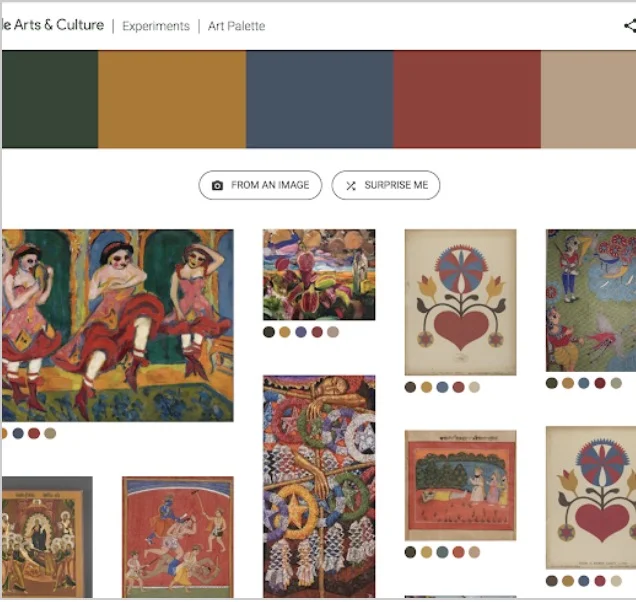
ART PALETTE
From web to interior design, color schemes play a fundamental role in creating cohesive user experiences, establishing brand identities and communicating moods or emotions. Art Palette uses machine learning to help creative experts explore palettes and make informed choices regarding color, and understand the context and history behind them.
A.I. Duet
This experiment lets you play a duet with the computer. Just play some notes, and the computer will respond to your melody. You can click the keyboard, use your computer keys, or even plug in a MIDI keyboard. It's just one example of how machine learning can inspire people to be creative in new ways.
Handwriting with a Neural Net
This experiment lets you play with a neural network that can generate strokes based on your handwriting style. Through interactive visualizations, you can see and explore how the neural net works. The visual output is particularly interesting because there’s so much interest in trying to understand and visualize neural networks.
Scribbling Speech
Language and images are closely intertwined: We think in pictures and we explain facts as spatial constellations. What if the spoken word could be transformed into dynamic visual worlds in real time? Speech input, machine learning and recurrent neural networks for image generation allow to com- puter generate complex imaginary worlds that follow the narrator and thus create complex animations controlled by linguistic structures.
Talk to Books
Talk to Books is an experimental new way to interact with books. Speak directly with all 100,000 books in Google’s index. Ask questions or make statements. The AI looks for sentences which are conversational responses. Read more here and check out Google Semantic Experiences to learn more about how this technology works.
NIMIIA CÉTIÏ BY JENNA SUTELA
Inspired by experiments in interspecies communication and aspiring to connect with a world beyond our consciousness, Nimiia documents the interactions between a neural network, audio recordings of early Martian language, and footage of the movements of extremophilic bacteria. The computer is a medium, channeling messages from entities that usually cannot speak.
DRAW TO ART
What if your sketches could help you discover great works of art? That’s the idea behind Draw to Art, and installation in the form of an easel. It uses machine learning to match your doodles to paintings, sculptures, and drawings from museums around the world.
spotify Discover Weekly
Rabid fans of Spotify have said that its music recommendation engine “knows me better than myself.” How can a machine possibly know what music you like – even better than you do? The key is a model that combines Collaborative Filtering, Natural Language Processing, and Audio Models – serving fresh sounds you’ll love every week.
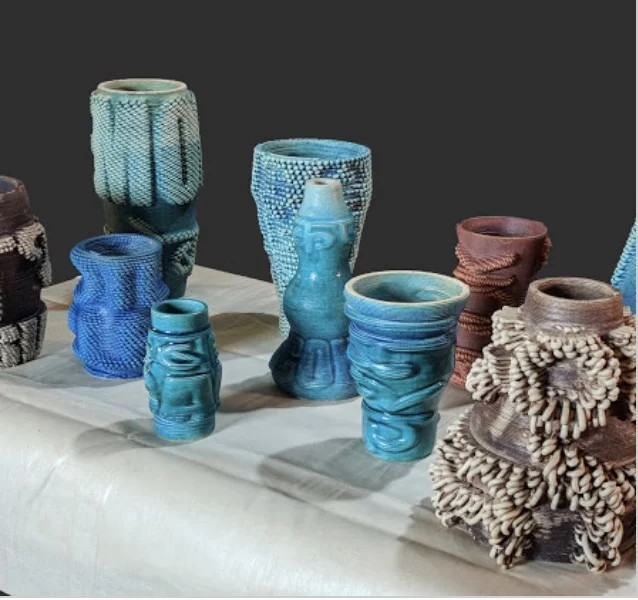
FUTURE RELICS
In a landmark exhibition in India, visitors were asked, “What object would you like archeologists 1000 years from now to remember our present day culture by?” Responses created an evolving data visualization and inspired a collection of 10 future relics, created using cutting edge 3D printing technology with Google ATAP and Emerging Objects, and glazed by an acclaimed master craftsman. The relics are now on display within the museums collection.
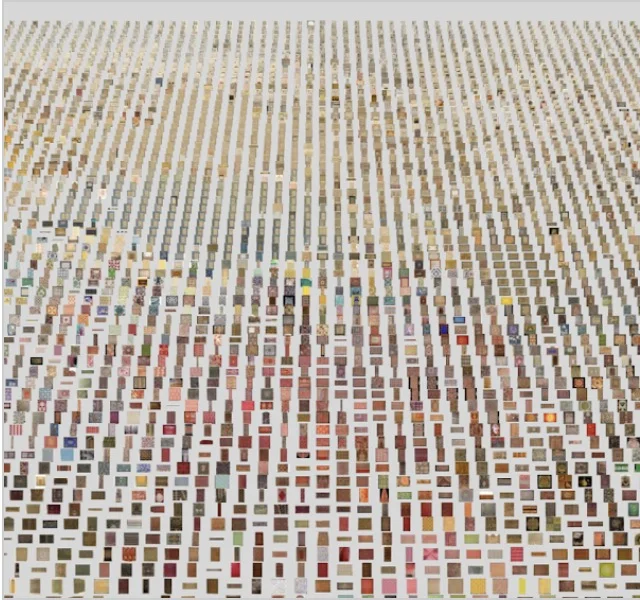
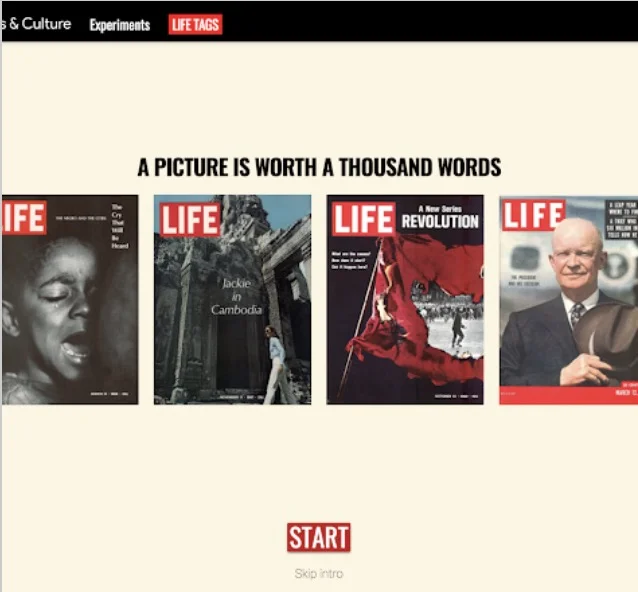
LIFE TAGS
Browse through the 20th century via Tags defined by Machine Learning. The project organizes over 4 million images from the Life magazine archives into an interactive encyclopedia. Life magazine was an American news publication with an emphasis on photojournalism. This experiment brings the iconic magazine to life. You can browse, search and rate images corresponding to thousands of labels as funny, right or wrong.
CURATOR TABLE
Inspired by curators around the world, the creators of Curator Table applied the principle of laying out prints on a table when planning an exhibition to their virtual gallery. Assets are animated in realtime. You can search objects, styles and artists, and view them in one 3D space.
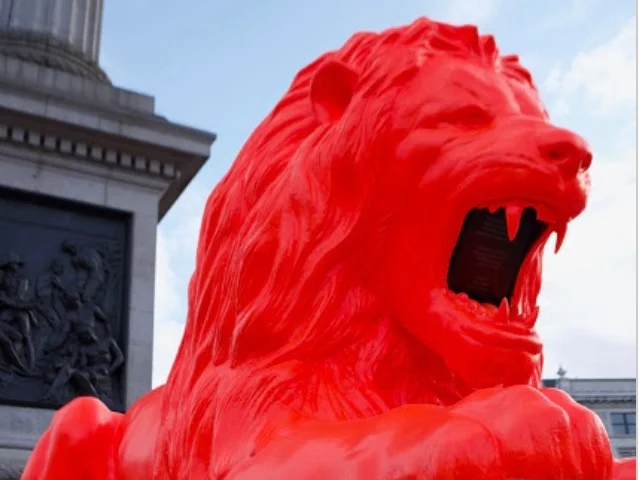
PLEASE FEED THE LIONS
This interactive public sculpture in Trafalgar Square is driven by machine learning. By daylight, an ever-evolving collective poem is shown on LEDs embedded in its mouth. By night, the poem is projection-mapped over the lion, a beacon of streaming text that invites others to join in and add their voice.
Netflix Recommendations
More than 80% of the TV shows watched on Netflix are found through its recommendation engine. That means the vast majority of the time, you’re letting a machine decide what to watch next. The secret sauce? A combination of machine learning and other technologies, which Netflix is constantly improving to bring the art of film to you.